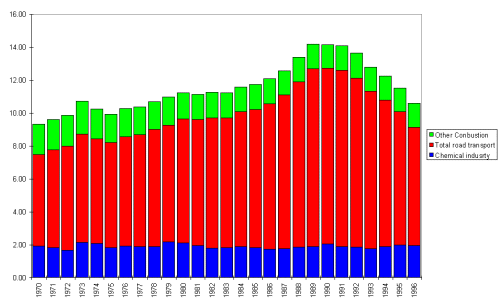
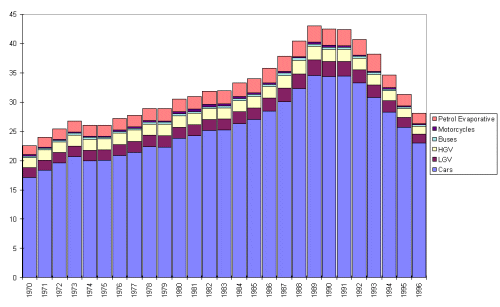
Emissions of benzene and 1,3 butadiene arise predominately from the evaporation and combustion of petroleum products. Benzene is contained in the petrol, and is present in both evaporative and tailpipe emissions, whereas 1,3-butadiene is only formed as a by-product of combustion. Petrol road vehicles contribute significantly to the total emissions of both these NMVOC species (60% and 59% of 1,3-butadiene and benzene respectively). Emissions have risen from 1970 to 1990 as a result of the increase in petrol vehicle use (figures 4.9 and 4.10). From 1991 the implementation of catalyst converters has reduced emissions from road transport. Table 4.9 and 4.10 show emissions from benzene and 1,butadiene from UK sources.
| Source | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 |
| Chemical Industry | ||||||
| 1,3-Butadiene manufacture | 1.04 | 1.16 | 1.12 | 1.04 | 1.07 | 1.06 |
| 1,3-Butadine use | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.88 |
| Total Chemical industry | 1.91 | 2.12 | 2.06 | 1.90 | 1.97 | 1.94 |
| Road Transport | ||||||
| Cars Petrol | 4.55 | 6.29 | 9.06 | 7.38 | 6.65 | 5.85 |
| Cars DERV | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| LGV Petrol | 0.46 | 0.53 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 0.46 | 0.4 |
| LGV DERV | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.19 |
| HGV Large | 0.1 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.21 |
| HGV Small | 0.29 | 0.3 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.3 | 0.27 |
| Buses | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Motorcycles | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.1 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 |
| Total road transport | 5.57 | 7.52 | 10.66 | 8.9 | 8.13 | 7.21 |
| Other transport | 1.85 | 1.61 | 1.45 | 1.44 | 1.41 | 1.45 |
| Total | 9.33 | 11.25 | 14.17 | 12.25 | 11.51 | 10.60 |
| UNECE source sectors | 1996 | as % |
| Comb. in Energy Prod & Transf. | 0.19 | 0.5% |
| Comb. in Comm/Inst/Resid/Agri | 1.32 | 3% |
| Combustion in Industry | 0.27 | 0.7% |
| Production Processes | 6.38 | 15% |
| Extr./Distrib. of Fossil Fuels | 0.59 | 1.4% |
| Road Transport | 26.32 | 64% |
| Other Transp & Machines | 3.62 | 9% |
| Waste Treatment & Disp. | 2.636 | 6% |
| Total | 41.33 | 100% |
Benzene and 1,3-butadiene emissions also arise as stack and more importantly, fugitive emissions from their manufacture and use in the chemical industry. Benzene is a major chemical intermediate, being used in the manufacture of many important chemicals including those used for the production of foams, fibres, coatings, detergents, solvents and pesticides. 1,3- butadiene is used in the production of various forms of synthetic rubber. Estimates for the industry are based on a few sets of reported data from large industrial plant and aggregated based on additional plant capacity and therefore have a high degree of uncertainty. In particular, there is considerable uncertainty associated with the fugitive component of emissions from chemical industry processes.